Furnace blowing cold air? Find out why and how to fix it.
Furnace blowing cold air should not be part of your worries after reading this pos.As winter’s chill descends upon us and the thermometer’s mercury takes a nosedive, one technological marvel stands tall as the unsung hero of cozy homes and comfortable workplaces: the furnace.
A furnace, in its essence, is more than just a metal box generating warmth; it’s a testament to human ingenuity, engineering prowess, and our unrelenting quest for comfort in the face of the harshest of seasons.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the inner workings of furnaces,the diverse types available, and their vital role in modern heating systems and possible reasons as why furnace blowing cold air.
Furnace blowing cold Air.
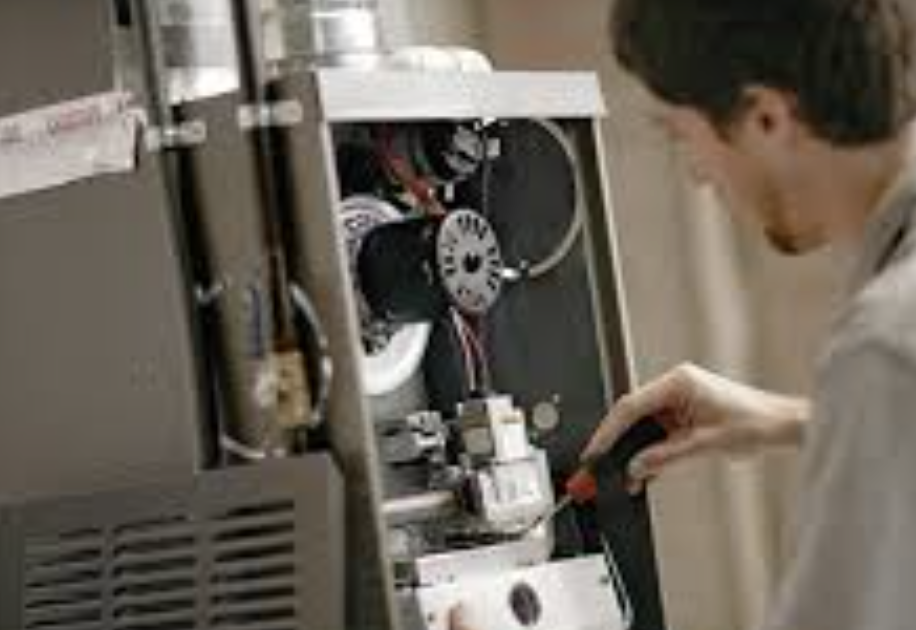

A furnace blowing cold air is a distressing problem in heating systems, especially during the cold months. This phenomenon occurs when a furnace fails to deliver warm air as expected, leaving occupants uncomfortable and potentially causing temperature-related issues.
Identifying and rectifying the root cause is essential to restore a comfortable indoor environment and ensure the efficient operation of the heating system.
Understanding why a furnace blows cold air is crucial for homeowners to address the problem promptly or seek professional assistance when necessary.
Furnace blowing cold air can be frustrating but if you want to make changes on your air conditioning devices,you may consider exploring more in-depth articles on 24000 btu air conditioner,18 000 btu air conditioner and smallest portable air conditioner.
In summary furnace blowing cold air can be one of the following: Thermostat issues,Clogged or Dirty Air Filters,Pilot Light or Ignition Problems,Thermocouple Malfunction,Blocked or Closed Vents,Blower Motor Problems,Pressure Switch and Venting Issues,Pressure Switch and Venting Issues,Fuel Supply Problems and Insufficient Maintenance.
These issues have been explained below;
Why is furnace blowing cold air
Thermostat Issues:
- Incorrect thermostat settings, such as being set to “cool” instead of “heat” or having a lower temperature setting, can lead to the furnace blowing cold air.
- Faulty thermostats may not accurately measure the room temperature, causing the heating system to misinterpret the need for warmth.
Clogged or Dirty Air Filters:
- Dirty or clogged air filters restrict airflow, leading to overheating in the furnace. To prevent damage, the furnace safety mechanism may activate, resulting in cold air blowing from the vents.
- Regularly replacing or cleaning air filters is essential to maintain proper airflow and heating efficiency.
Pilot Light or Ignition Problems:
- In gas furnaces, a malfunctioning pilot light or ignition system can prevent the furnace from igniting. Without ignition, no heat is produced, resulting in cold air circulation.
- Common issues include a faulty pilot light, a dirty or damaged ignition sensor, or gas supply problems.
Thermocouple Malfunction:
- In gas furnaces, the thermocouple is responsible for keeping the gas valve open. If it malfunctions, the gas valve may close prematurely, preventing ignition and warm air production.
Blocked or Closed Vents:
- Closed or obstructed supply and return vents can disrupt the airflow in the HVAC system. This imbalance can lead to temperature inconsistencies and cold air being pushed from the vents.
Blower Motor Problems:
- A malfunctioning blower motor may not circulate warm air effectively. Issues can arise from electrical problems, worn-out bearings, or a faulty motor capacitor.
Pressure Switch and Venting Issues:
- High-efficiency gas furnaces may have pressure switches that monitor proper ventilation. Issues with these switches or blockages in the venting system can cause the furnace to shut down to ensure safety, resulting in cold air blowing.
Fuel Supply Problems:
- Gas furnaces require a steady supply of fuel. Any issues with the gas line, gas valve, or gas pressure can disrupt the heating process.
Faulty Thermostat Wiring or Control Board:
- Wiring problems or issues with the control board can disrupt communication between the thermostat and the furnace. This miscommunication can prevent the furnace from igniting and producing heat.
Insufficient Maintenance:
- Neglected maintenance can lead to various problems within the furnace. Components may become dirty, corroded, or worn out, leading to poor performance and cold air issues.
Also read: Direction of Furnace Filter
What does a furnace do
A furnace is a crucial home heating system that operates by generating and distributing warm air throughout a building.
It serves to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature during cold weather by utilizing a heat source, such as natural gas, propane, electricity, or oil, to produce heat.
The furnace’s primary function is to heat the air and then circulate it through a network of ducts and vents, delivering warmth to various rooms or spaces within a home or commercial building.
This essential appliance plays a pivotal role in ensuring indoor comfort, especially in regions with cold winters, by providing a consistent and controlled source of heat.
What is a furnace filter
A furnace filter is a critical component in a heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system, designed to enhance indoor air quality.
It serves as a barrier that captures and traps airborne particles, including dust, pollen, pet dander, and other contaminants, as the system circulates air.
This filtration process helps remove allergens and pollutants, preventing them from entering the living space.
Regularly replacing or cleaning the filter is essential to maintain the efficiency of the HVAC system, as a clogged filter can reduce airflow, strain the system, and lead to higher energy consumption.
A clean furnace filter not only ensures healthier indoor air but also prolongs the life of the HVAC equipment.
Difference between Air Filter and Furnace Filter
Air Filter vs. Furnace Filter:
Purpose:
- Air Filter: Primarily focuses on improving indoor air quality by capturing airborne contaminants in residential or commercial spaces.
- Furnace Filter: Specifically designed to protect the HVAC system by preventing dust and debris from entering and damaging its components.
Location:
- Air Filter: Installed in various locations, including air purifiers, standalone filtration systems, or within HVAC systems.
- Furnace Filter: Positioned within the HVAC system, typically near the air intake.
Filtration Efficiency:
- Air Filter: Emphasizes higher filtration efficiency to remove allergens, pollutants, and fine particles from the indoor air.
- Furnace Filter: Prioritizes capturing larger particles like dust and debris to protect the HVAC system.
Frequency of Replacement:
- Air Filter: Replacement frequency varies based on the type and usage, typically ranging from monthly to annually.
- Furnace Filter: Usually requires replacement every one to three months, with some high-efficiency filters lasting longer.
Material and Design:
- Air Filter: Constructed with various filtration media, including HEPA, activated carbon, or electrostatic materials, tailored for specific indoor air quality needs.
- Furnace Filter: Designed with materials that can withstand the airflow and temperature conditions within the HVAC system, focusing on system protection.
Effect on HVAC System:
- Air Filter: Primarily impacts indoor air quality and may have minimal effect on HVAC system performance.
- Furnace Filter: Directly affects HVAC system efficiency and longevity, with a clogged filter reducing airflow and causing strain on the system.
Cost:
- Air Filter: Costs vary based on the type and brand but often come at a higher price point, especially for specialized filtration needs.
- Furnace Filter: Generally, more cost-effective, with a focus on maintaining HVAC system integrity.
How many Filters does a Furnace have
A furnace typically has one primary filter, commonly known as the furnace filter or air filter. This filter is located within the HVAC system, usually near the air intake.
Its primary function is to capture dust, debris, and other larger particles from the incoming air, preventing them from entering the furnace and potentially damaging its components.
While some advanced HVAC systems may incorporate additional filters or air purification systems for improved air quality, the standard setup consists of a single furnace filter.
Regular maintenance, including changing or cleaning this filter as needed, is crucial to ensure efficient furnace operation and prolong the lifespan of the HVAC system.
Can you run your Furnace without a Filter
Running a furnace without a filter is not recommended. The furnace filter plays a vital role in preventing dust, debris, and particles from entering the HVAC system.
Without a filter, these contaminants can accumulate on sensitive components, such as the blower motor and heat exchanger, causing damage and reducing efficiency.
Additionally, a missing filter can lead to poor indoor air quality as airborne particles are not filtered out.
While a furnace may technically run without a filter, it is likely to result in higher maintenance costs, reduced efficiency, and potential health issues due to degraded air quality.
Regularly replacing or cleaning the filter is essential for proper furnace operation and indoor comfort.
How many Filters should a Furnace have
A furnace typically has one primary filter, commonly known as the furnace filter or air filter. This filter is located within the HVAC system, usually near the air intake.
Its primary function is to capture dust, debris, and other larger particles from the incoming air, preventing them from entering the furnace and potentially damaging its components.
While some advanced HVAC systems may incorporate additional filters or air purification systems for improved air quality, the standard setup consists of a single furnace filter.
Regular maintenance, including changing or cleaning this filter as needed, is crucial to ensure efficient furnace operation and prolong the lifespan of the HVAC system.
How do I clean my Furnace Filter
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Safety First:
Ensure the furnace is turned off, and wait for it to cool down if it has been running.
Locate the Filter:
Find the filter’s location, usually near the return air duct or blower compartment.
Remove the Filter:
Carefully slide or unclip the filter from its slot.
Inspect the Filter:
Examine the filter for dirt and debris. If it’s excessively dirty or damaged, consider replacing it instead.
Cleaning Options:
- Vacuum: Use a vacuum cleaner with a brush attachment to gently remove surface dust and particles.
- Soak: If the filter is washable, soak it in warm water with mild detergent for about 15 minutes. Rinse thoroughly and let it dry completely before reinstalling.
Dry the Filter:
Ensure the filter is completely dry to prevent mold growth. Air drying is usually best.
Reinstall the Filter:
Slide or clip the clean and dry filter back into its original position, ensuring it’s facing the correct direction (arrows indicating airflow direction).
Turn On the Furnace:
Power up the furnace once the filter is securely in place.
Regular Maintenance:
Establish a schedule for filter maintenance, typically every one to three months, depending on usage and filter type.
How do I know if my Furnace Filter is good
- Clean Appearance: A visually clean filter without excessive dust or debris.
- Efficient Airflow: Consistent and strong airflow through the vents.
- Even Heating: Maintained and even distribution of warm air throughout the home.
- Low Energy Bills: An efficient filter contributes to lower heating costs.
- Minimal Allergens: Reduced allergens in the indoor air.
- No Unusual Sounds: The absence of unusual sounds like whistling or rattling.
- Proper Sizing: A filter that fits snugly in its housing without gaps.
- Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Adherence to recommended replacement or cleaning schedules.
- No Unusual Odors: The absence of unusual or musty odors from the HVAC system.
- System Longevity: A well-maintained filter prolongs the life of the furnace and other HVAC components.
Do all Furnaces have a Filter
Not all furnaces have a filter as a standard feature. The presence of a filter depends on the type and design of the furnace.
Many modern forced-air furnaces, especially those used in residential heating systems, come equipped with filters to improve indoor air quality and protect the HVAC system. However, certain furnace types, such as gravity furnaces, may lack a filter.
Additionally, in some older or basic models, filters may not be included, though they can often be added for improved air quality and system longevity.
It’s crucial to check your furnace’s specifications and, if necessary, consult with a professional to determine whether your furnace has a filter and its maintenance requirements.
How long can a Furnace run without a Filter
Running a furnace without a filter is not recommended, and it should be avoided whenever possible.
The presence of a filter is crucial for protecting the HVAC system and maintaining indoor air quality. Here’s why:
- HVAC System Protection: A filter prevents dust, debris, and particles from entering the HVAC system. Without a filter, these contaminants can accumulate on sensitive components, like the blower motor and heat exchanger, potentially causing damage over time.
- Air Quality: Filters also help improve indoor air quality by capturing airborne particles. Running a furnace without a filter can result in reduced air quality, potentially leading to health issues, especially for individuals with allergies or respiratory problems.
- Efficiency: A clogged filter can reduce airflow, causing the furnace to work harder and less efficiently. This can result in higher energy bills and decreased system lifespan.
In an emergency situation where a filter is temporarily unavailable, it’s best to limit furnace operation until a filter can be installed.
Running a furnace for an extended period without a filter is not advisable and can lead to system damage and reduced performance.
Types of Furnaces Filters
Fiberglass Filters:
- Cost-effective and commonly used.
- Basic filtration, effective against larger particles.
- Need frequent replacement, typically every 1-2 months.
Pleated Filters:
- Provide better filtration with a larger surface area.
- Capture smaller particles like dust, pollen, and pet dander.
- Last longer, typically replaced every 3-6 months.
HEPA Filters:
- High-efficiency particulate air filters.
- Exceptional at trapping microscopic allergens and pollutants.
- Ideal for allergy sufferers but require frequent replacement due to reduced airflow.
Washable Filters:
- Reusable, made of durable materials.
- Need regular cleaning but offer long-term cost savings.
- Environmentally friendly option.
Electrostatic Filters:
- Use static electricity to attract and trap particles.
- Effective against various contaminants, including smoke and bacteria.
- Available in both disposable and washable versions.
Activated Carbon Filters:
- Utilize activated carbon to adsorb odors and chemicals.
- Commonly used in combination with other filter types.
- Ideal for improving indoor air quality.
UV Filters:
- Use ultraviolet light to kill bacteria and mold.
- Installed within HVAC systems to enhance air quality.
- May require professional installation and maintenance.
MERV Ratings:
- Filters are rated on the Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value (MERV) scale.
- Higher MERV ratings indicate better filtration, but also potential for reduced airflow.
- Choose a MERV rating based on your specific air quality needs and HVAC system capacity.
What happens when a Furnace Filter is dirty.
When a furnace filter becomes dirty or clogged, it can lead to several issues that affect both the HVAC system and indoor air quality. Here’s what happens when a furnace filter is dirty:
- Reduced Airflow: A dirty filter restricts the flow of air through the HVAC system. This reduction in airflow can lead to several problems.
- Overheating: The restricted airflow causes the furnace to work harder to heat or cool your home. This can result in the system overheating, potentially leading to system shutdowns and costly repairs.
- Decreased Efficiency: A clogged filter makes the HVAC system less efficient, as it requires more energy to circulate air. This inefficiency leads to higher energy bills.
- Poor Indoor Air Quality: A dirty filter is less effective at trapping dust, pollen, pet dander, and other airborne particles. As a result, these contaminants can circulate freely in your home, leading to reduced indoor air quality and potential health issues, especially for allergy sufferers.
- Shortened Lifespan: The strain caused by reduced airflow and increased energy consumption can shorten the lifespan of the HVAC system, leading to the need for premature repairs or replacement.
- Uncomfortable Temperatures: Inconsistent heating or cooling due to reduced airflow can result in uncomfortable indoor temperatures and temperature variations throughout the home.
- Frozen Evaporator Coils: In air conditioning systems, reduced airflow can cause the evaporator coils to freeze, leading to system malfunctions.
How do I know if my furnace filter is clogged
- Reduced Airflow:
The most common sign is a noticeable reduction in the airflow coming from your vents. If the airflow feels weaker than usual, it could be due to a clogged filter.
- Uneven Heating or Cooling:
Rooms in your home may experience inconsistent temperatures. Some may be warmer than others because the clogged filter restricts airflow, preventing even distribution of heated or cooled air.
- Higher Energy Bills:
A clogged filter causes your HVAC system to work harder to maintain the desired temperature, resulting in increased energy consumption and higher utility bills.
- Dust and Allergens:
If you notice an increase in dust, allergens, or pet dander in your home, it may be a sign that the filter is no longer effectively capturing these particles.
- Unusual Sounds:
A clogged filter can cause strange noises like whistling or rattling from the HVAC system as it struggles to draw in air.
- Short Cycling:
Short cycling refers to the furnace turning on and off more frequently than usual. A clogged filter can overheat the system, leading to this behavior.
- Visible Dirt and Debris:
In some cases, you can visually inspect the filter. If it appears visibly dirty, covered in dust, or discolored, it’s a clear sign that it needs attention.
- Odors:
A clogged filter can lead to musty or stale odors coming from your HVAC system due to reduced airflow and potential mold growth.
Can dirty Filter stop Furnace from turning on
Yes, a dirty or clogged furnace filter can prevent the furnace from turning on or cause it to shut down shortly after starting.
What are the symptoms of a bad air filter
- Reduced Airflow: One of the most noticeable signs is decreased airflow from vents.
- Uneven Heating or Cooling: Rooms may have inconsistent temperatures due to restricted airflow.
- Increased Energy Bills: A clogged filter forces the HVAC system to work harder, leading to higher energy costs.
- Dusty and Allergenic Air: More dust and allergens in the air as the filter fails to trap particles effectively.
- Unusual Sounds: Whistling or rattling noises may occur as the system struggles to pull in air.
- Short Cycling: The furnace or AC may turn on and off frequently, impacting efficiency.
- Odors: Musty or stale smells from reduced airflow and potential mold growth.
Conclusion
A furnace filter serves as a critical component in both maintaining indoor air quality and ensuring the efficient operation of your HVAC system.
Recognizing the symptoms of a bad or clogged air filter is crucial for homeowners to address issues promptly and avoid potential consequences.
Reduced airflow, uneven heating or cooling, and increased energy bills are clear indicators of filter problems.
Additionally, a dirty filter can lead to a dustier and less allergen-free home environment, as it fails to effectively trap particles.
Unusual sounds and short cycling may also signal filter issues, affecting the overall efficiency of your HVAC system.
Moreover, neglecting a clogged filter can result in overheating, premature system wear, and even system shutdowns due to safety mechanisms.
Proper maintenance, including regular cleaning or replacement of the filter, is essential to prevent these problems.
In essence, the health of your HVAC system and the quality of the air you breathe are closely tied to the condition of your furnace filter.
By staying vigilant and addressing filter issues promptly, homeowners can ensure not only comfortable indoor environments but also long-term energy and cost savings.
Prioritizing filter maintenance is a simple yet effective way to keep your HVAC system running smoothly and maintain a healthier home.Let’s hope you will not find yourself in cold air again.